JavaEE7 で CDI の Interceptor を味わってみる
Java EE6 から導入された CDI のインターセプタだが( JavaEE5 までは EJB インターセプタしか存在しなかった)、JavaEE7 で改良が加えられているので紹介する。今回紹介する内容は以下の二点になる。
- インターセプタに優先順位が付けられる様になった
- 54.2.5 Ordering Interceptors https://docs.oracle.com/javaee/7/tutorial/interceptors002.htm#GKEDM
- beans.xml に インターセプタクラスを登録する必要がなくなった
- CDI 1.2 is released http://www.cdi-spec.org/news/2014/04/14/CDI-1_2-released/
こちらをそれぞれ試してみる
ソースコード
今回作成したソースコードの動作イメージは以下となる。
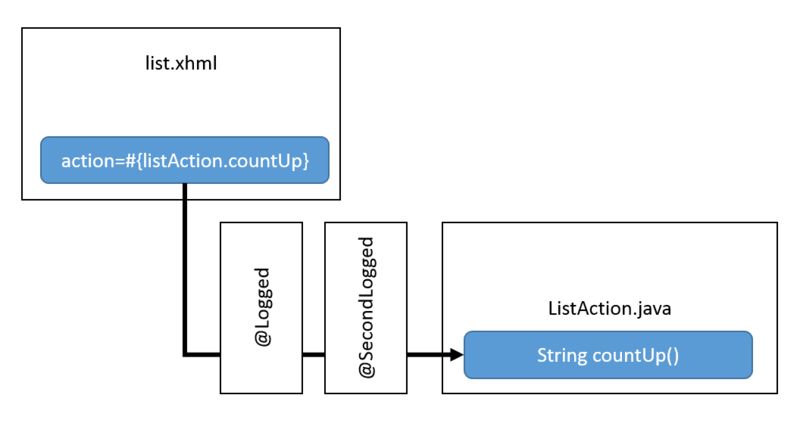
次に、動作に必要なソースコードは以下になる。beans.xml が不要な点に注意が必要だ。
- list.xhtml
<?xml version='1.0' encoding='UTF-8' ?> <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd"> <html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" xmlns:h="http://xmlns.jcp.org/jsf/html" xmlns:f="http://xmlns.jcp.org/jsf/core"> <h:head> <title>Facelet のインターセプタを学ぶ</title> </h:head> <h:body> <h:form> Hello Facelets: 今は <h:outputText value="#{listAction.count}" />回目<br /> <h:commandButton value="加算" action="#{listAction.countUp()}" /> </h:form> </h:body> </html>
- Logged.java
package com.mydomain.annotations; import java.lang.annotation.ElementType; import java.lang.annotation.Inherited; import java.lang.annotation.Retention; import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy; import java.lang.annotation.Target; import javax.interceptor.InterceptorBinding; @Inherited @InterceptorBinding @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE}) public @interface Logged { }
- SecondLogged.java
package com.mydomain.annotations; import java.lang.annotation.ElementType; import java.lang.annotation.Inherited; import java.lang.annotation.Retention; import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy; import java.lang.annotation.Target; import javax.interceptor.InterceptorBinding; @Inherited @InterceptorBinding @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE}) public @interface SecondLogged { }
- LoggedInterceptor.java
package com.mydomain.interceptors; import com.mydomain.annotations.Logged; import java.io.Serializable; import javax.annotation.Priority; import javax.interceptor.AroundInvoke; import javax.interceptor.Interceptor; import javax.interceptor.InvocationContext; @Priority(Interceptor.Priority.LIBRARY_BEFORE) @Interceptor @Logged public class LoggedInterceptor implements Serializable { public LoggedInterceptor() { } @AroundInvoke public Object logMethodEntry(InvocationContext ic) throws Exception { System.out.println("$$Logged Interceptor, before: " + ic.getMethod().getName() + " in class " + ic.getMethod().getDeclaringClass().getName()); Object obj = ic.proceed(); System.out.println("$$Logged Interceptor, after: " + ic.getMethod().getName() + " in class " + ic.getMethod().getDeclaringClass().getName()); return obj; } }
- SecondLoggedInterceptor.java
package com.mydomain.interceptors; import com.mydomain.annotations.SecondLogged; import java.io.Serializable; import javax.annotation.Priority; import javax.interceptor.AroundInvoke; import javax.interceptor.Interceptor; import javax.interceptor.InvocationContext; @Priority(Interceptor.Priority.APPLICATION) @Interceptor @SecondLogged public class SecondLoggedInterceptor implements Serializable { @AroundInvoke public Object logMethodEntry(InvocationContext ic) throws Exception { System.out.println("@@SecondLogged Interceptor, before: " + ic.getMethod().getName() + " in class " + ic.getMethod().getDeclaringClass().getName()); Object obj = ic.proceed(); System.out.println("@@SecondLogged Interceptor, after: " + ic.getMethod().getName() + " in class " + ic.getMethod().getDeclaringClass().getName()); return obj; } }
- ListAction.java
package com.mydomain.action; import com.mydomain.annotations.SecondLogged; import com.mydomain.annotations.Logged; import java.io.Serializable; import javax.faces.view.ViewScoped; import javax.inject.Named; @Named @ViewScoped public class ListAction implements Serializable { private int count; @Logged @SecondLogged public String countUp() { System.out.println("★★★ListAction#countUp, count = " + count); setCount(getCount() + 1); return ""; } public int getCount() { return count; } public void setCount(int count) { this.count = count; } }
上記を動作させた場合の実行結果はいかになる。
情報: $$Logged Interceptor, before: countUp in class com.mydomain.action.ListAction 情報: @@SecondLogged Interceptor, before: countUp in class com.mydomain.action.ListAction 情報: ★★★ListAction#countUp, count = 0 情報: @@SecondLogged Interceptor, after: countUp in class com.mydomain.action.ListAction 情報: $$Logged Interceptor, after: countUp in class com.mydomain.action.ListAction
インターセプタの順番を決める Priority は値が大きいほど優先度が高く、あらかじめ用意されている定数は以下になる。
| 定数名 | 値 |
| PLATFORM_BEFORE | 0 |
| LIBRARY_BEFORE | 1000 |
| APPLICATION | 2000 |
| LIBRARY_AFTER | 3000 |
| PLATFORM_AFTER | 4000 |